Driving Digital Transformation: How Michelin Leverages ServiceNow for IT, HR, CMDB and AI Innovation

ServiceNow is a leading cloud-based or on-premises platform designed to automate and optimize enterprise workflows across IT, HR, customer service, and other business functions. By centralizing processes and leveraging AI-driven capabilities, it helps organizations improve efficiency, enhance user experiences, and accelerate digital transformation. With its scalable architecture and robust integration options, ServiceNow enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce manual tasks, and deliver consistent, high-quality services.
ServiceNow at Michelin
Michelin faced challenges managing IT services and workflows across a complex global ecosystem, relying on fragmented tools like emails, spreadsheets and providers' tools. A major gap was in Asset and Configuration Management (CMDB), leading to incomplete inventories, poor risk assessment, and delays in incident and change management.
To address this, Michelin implemented ServiceNow as a centralized platform for ITSM and enterprise workflow automation. ServiceNow provides a single source of truth, enabling standardisation, automation, and improved governance. Key goals include:
- Enhanced visibility into IT operations
- Reduced manual effort through automation
- Robust CMDB for asset and components for tracking and impact analysis
- Unified platform for multiple business functions
This supports Michelin’s digital transformation strategy, driving scalability and agility across global operations from more than five years.
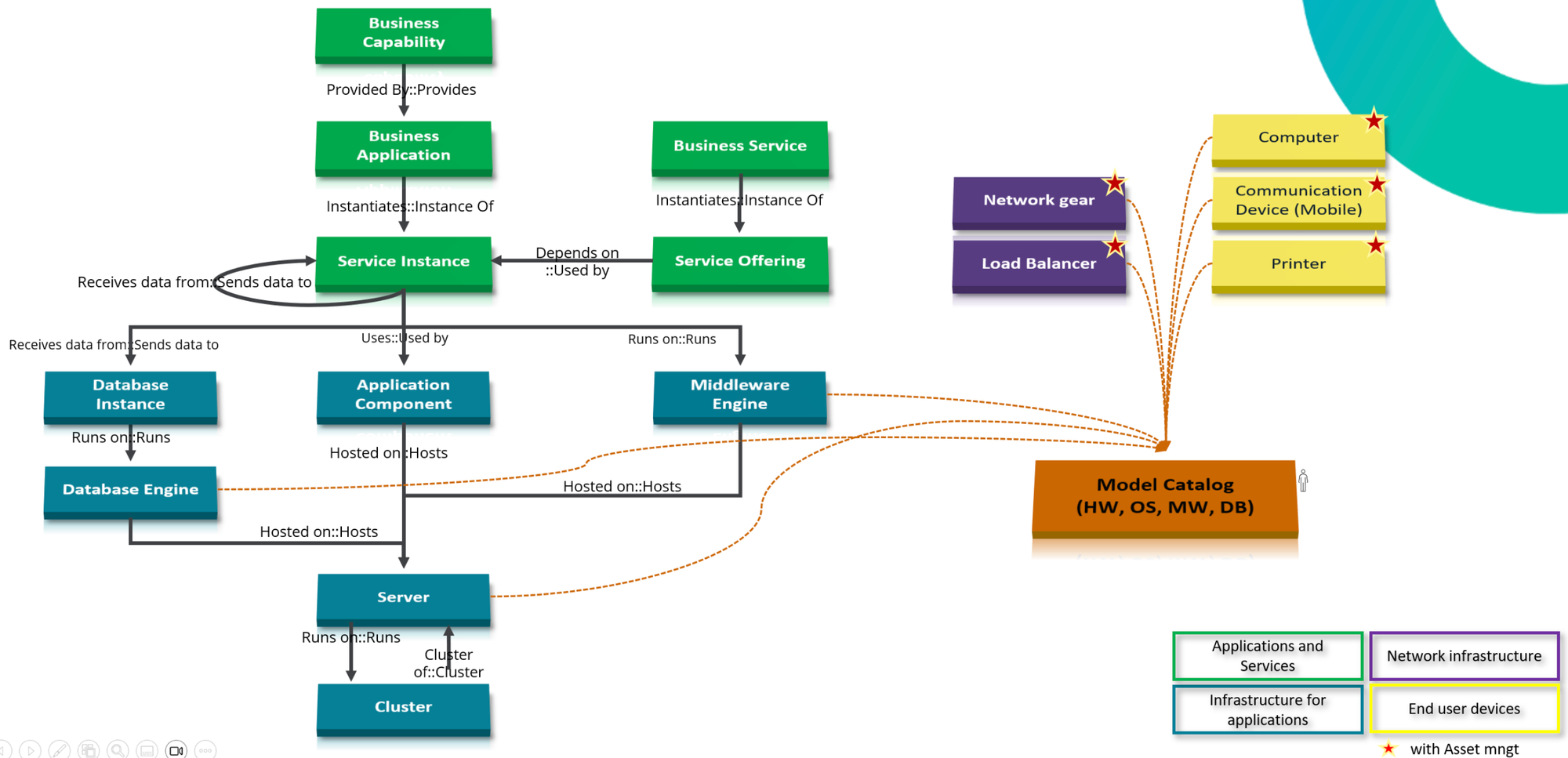
The corner stone: the CMDB
ServiceNow’s CMDB architecture at Michelin provides a structured and dynamic representation of IT assets components and their interdependencies. The model begins with Business Capabilities and Applications, which instantiate Service Instances and Service Offerings, linking business services to technical components. At the infrastructure layer, Database Engines, Application Components, Middleware, and Servers are mapped to clusters, ensuring clarity on hosting relationships and data flows. This hierarchy extends to Network Gear, Load Balancers, and end-user devices such as Computers, Printers, and Mobile Communication Devices, all cataloged under a unified Model Catalog (HW, OS, MW, DB). By maintaining these relationships, Michelin achieves accurate impact analysis, risk assessment, and change planning. This structured approach reduces errors during incident resolution, supports compliance, and enables proactive governance across applications, infrastructure, and end-user assets.
What Service Now brings to the table
End User Experience
Employees begin their experience with a self-service portal offering access to knowledge bases, service catalogs, request forms, and a virtual agent that fosters greater autonomy.
Scalability
Michelin’s global footprint demands solutions that can scale effortlessly. ServiceNow’s modular architecture allowed us to add new functionalities as business needs evolved—whether it was expanding ITSM capabilities or integrating HR workflows. This flexibility ensured that the platform could grow with Michelin’s strategic ambitions.
Automation and Efficiency
Service delivery became faster and more accurate with automated workflows, reducing errors and speeding up incident resolution, change approvals, and requests—boosting IT efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Human Resources Process Automation
Beyond IT, ServiceNow streamlined HR processes by enabling automation and improving employee engagement. One key benefit was the ability to pass on Michelin’s benefits to employees through HR workflows, ensuring that perks, programs, and policies were communicated and delivered efficiently. This automation reduced manual effort, improved employee satisfaction, and maintained compliance with HR standards across global operations.
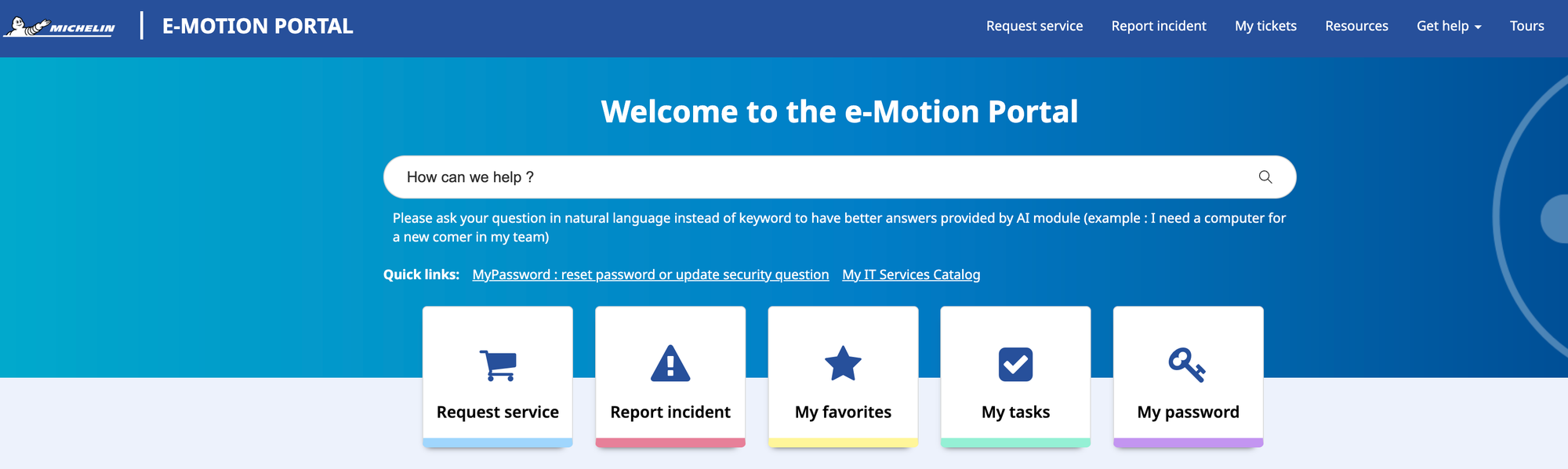
e-Motion Portal: A Modern Employee Experience on top of ServiceNow
Michelin’s e-Motion Portal is a customized, user‑friendly front-end built on the ServiceNow platform to enhance the employee experience. Designed specifically for Michelin’s internal needs, the portal provides a unified digital entry point for employees across the organization.
A Unified Self-Service Experience
Emotion Portal enables Michelin employees to easily:
- Access HR and IT services
- Submit requests and incidents
- Browse knowledge articles
- Interact with automated workflows
- Provide feedback or track ongoing requests
This creates a streamlined, intuitive self-service environment that reduces dependency on support teams and improves response efficiency.
Built on ServiceNow’s Service Portal Framework
e-Motion Portal is built using a modern, modular web framework designed to deliver responsive, user-friendly interfaces. Its foundation includes several key technologies:
- AngularJS – Serves as the core client-side framework, powering widget logic, data binding, and interactive behaviors within the portal.
- Bootstrap 3 – Provides the responsive grid system and layout components, ensuring that portals render consistently across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices.
- JavaScript – Used for both client-side scripting in AngularJS controllers and server-side scripting through ServiceNow APIs.
- HTML/CSS with SASS – Handles structure and styling, with SASS enabling flexible theme customization across portals.
- ServiceNow Platform APIs – Includes tools like GlideRecord for database operations and GlideAjax for asynchronous client-server communication.
How e‑Motion handles API Consumption
In e‑Motion, external API consumption is managed through a custom Service Portal widget. The process involves four streamlined steps
- Configure the REST Message
Create a REST Message in System Web Services → Outbound → REST Message. Add the target API endpoint and required headers. - Define HTTP Methods
Within the REST Message, configure the needed methods (GET, POST, etc.). ServiceNow provides a Preview Script Usage option to generate server‑side code for each method. - Execute API Logic in a Widget
In the Service Portal widget, the Server Script runs the API call usingRESTMessageV2. The widget parses the API’s JSON or XML response and prepares it for display. - Render Data in the Client/UI
The processed data is passed from the server script to the Client Controller and displayed in the widget’s HTML template.
The classic example is MS teams integration :
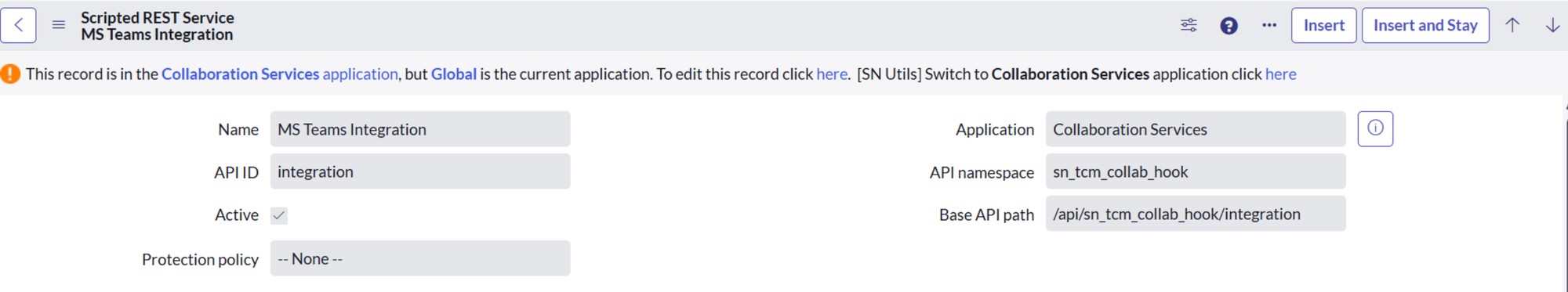
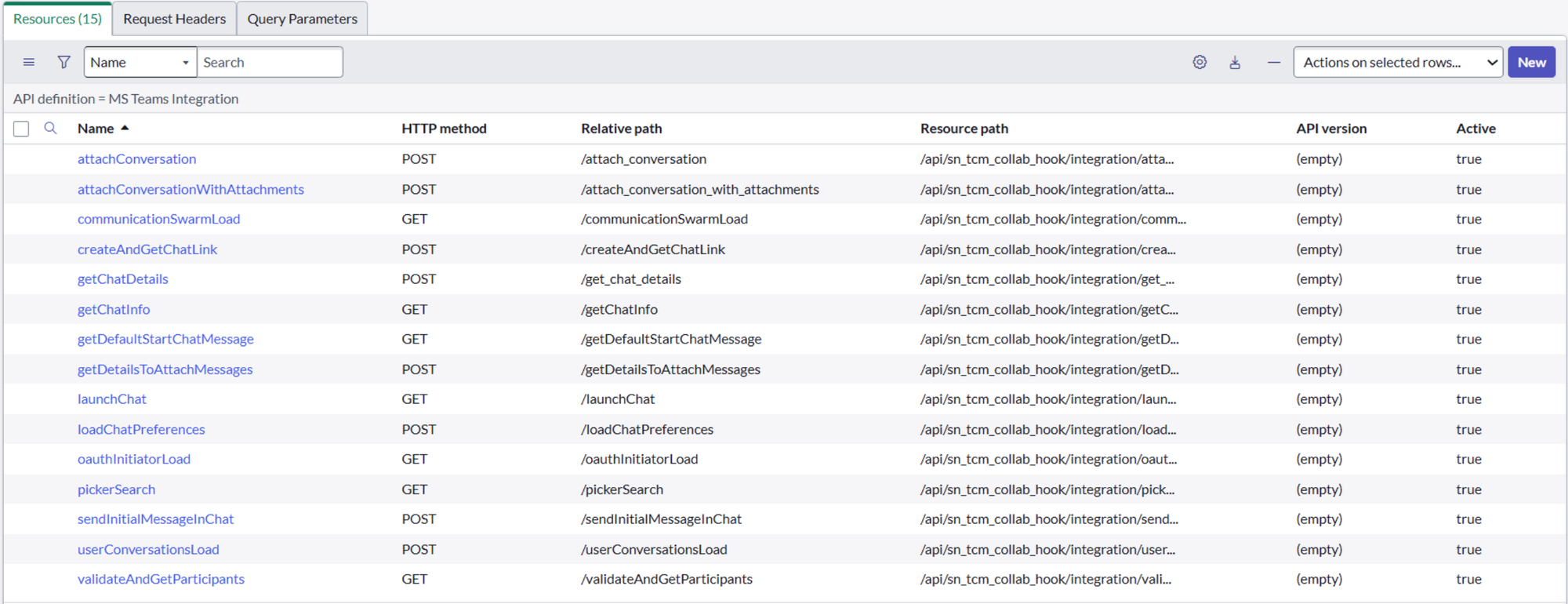
Exposing ServiceNow data
Given how we use ServiceNow and its scale at Michelin, we had to expose data in our datalake. The ServiceNow-to-CorporateDataLake data ingestion process evolved multiple times to improve performance, accuracy, and scalability.
REST API (Python) – Initial Approach
The pipeline originally used REST APIs with pagination, which resulted in:
- Missing records and updates
- No handling of deleted records, causing excess data in the datalake.
- Long daily load times
ServiceNow Kafka Connector
Moving to the ServiceNow Kafka Connector introduced event-driven ingestion with:
- Real‑time data updates
- Capture of delete events
- Improved data quality
Confluent Kafka Connector – Final Solution
To overcome ServiceNow platform limits and growing data volume, the pipeline migrated to the Confluent Kafka Connector, delivering:
- No bottlenecks and more efficient data loads (including the capacity to handle large payloads) reducing the ingestion lag
- Separation of concerns using Kafka namespace
- Automatic schema handling aligned with ServiceNow
- Lower latency and fewer restrictions from ServiceNow APIs
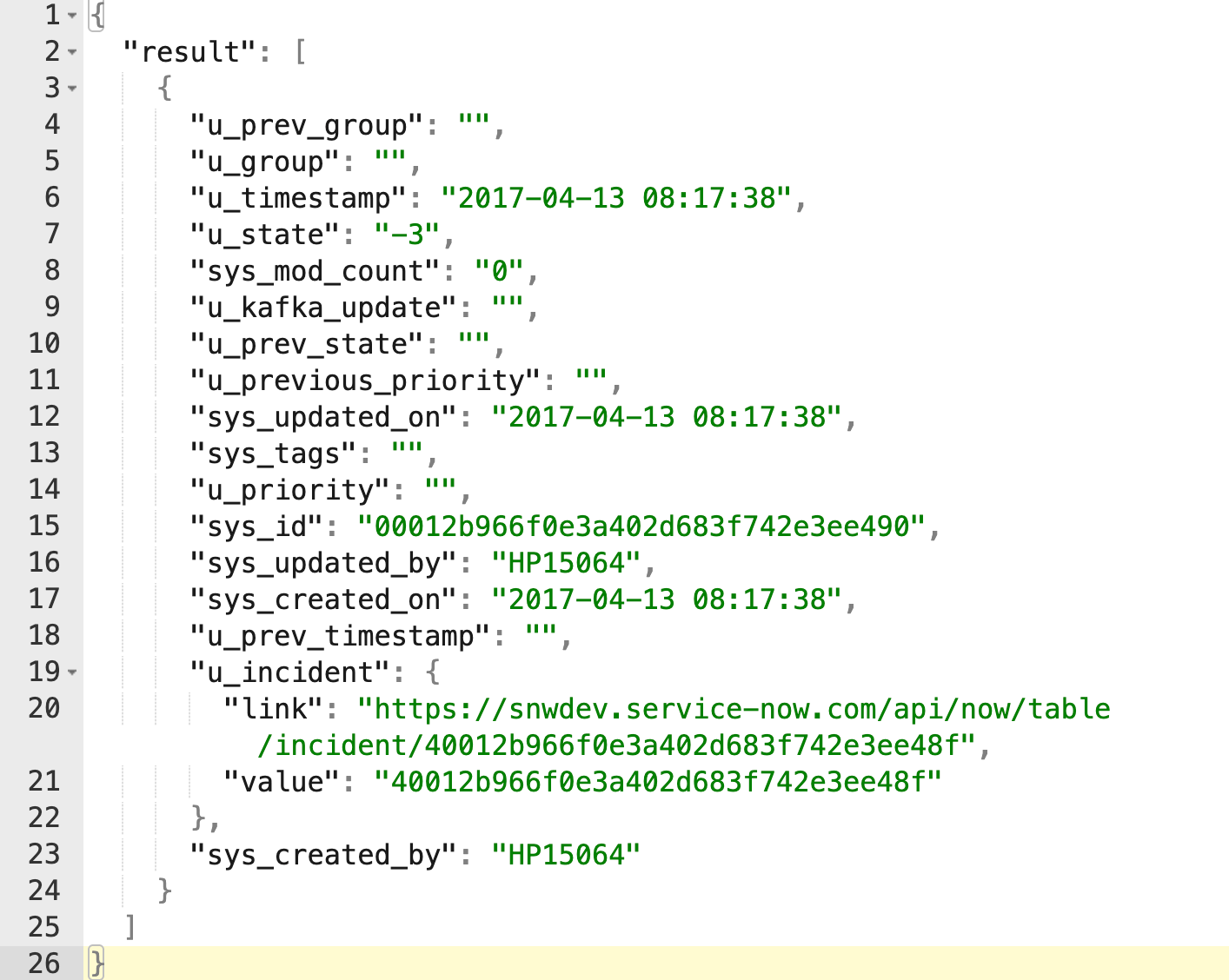
Kafka serves as a temporary storage and we use stream processing to handle high‑velocity and high‑volume operational data streams. Data from Kafka topics is pulled as continuous streams into the Corporate Data Lake (CDL), where it is used for analytics, reporting, and downstream processing.
Automation with Service Now
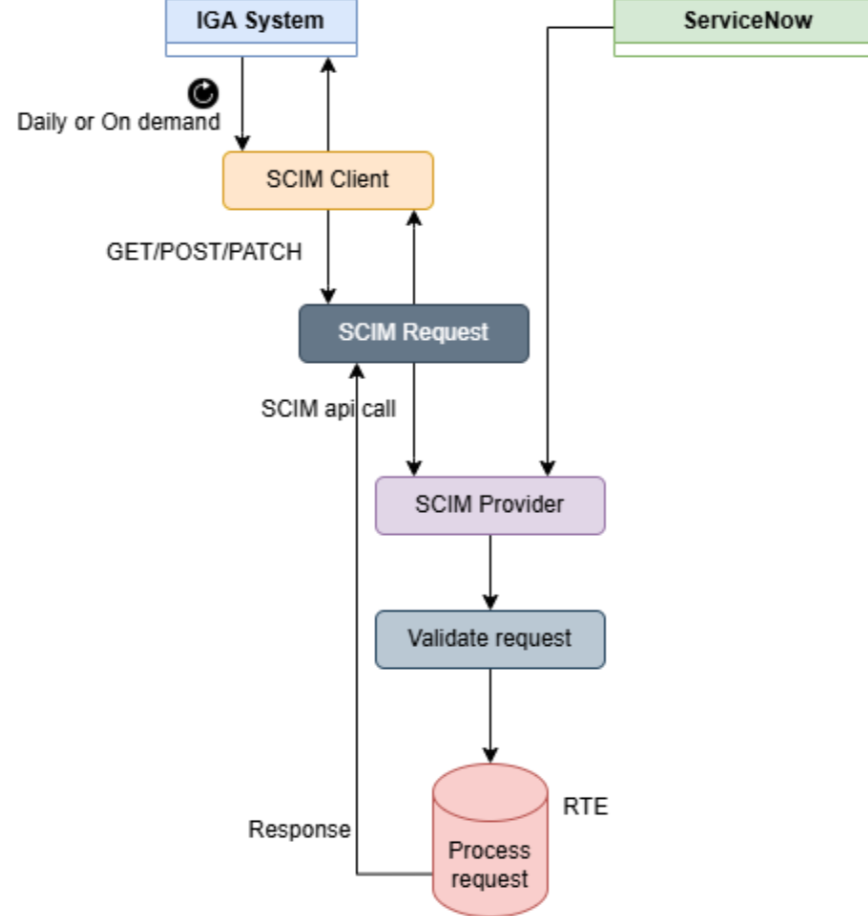
ServiceNow- IGA Integration
- ServiceNow provides an out‑of‑the‑box SCIM plugin, which includes a full suite of APIs supporting the SCIM protocol for identity provisioning.
- A SCIM Client sends provisioning requests to ServiceNow, including create, update, and delete operations for users.
- ServiceNow acts as the SCIM Provider, receiving these requests through its SCIM API and managing user accounts within the platform.
- The SCIM API exposes standardized endpoints to perform CRUD operations (create, read, update, delete) on users and groups, following the SCIM protocol specifications.
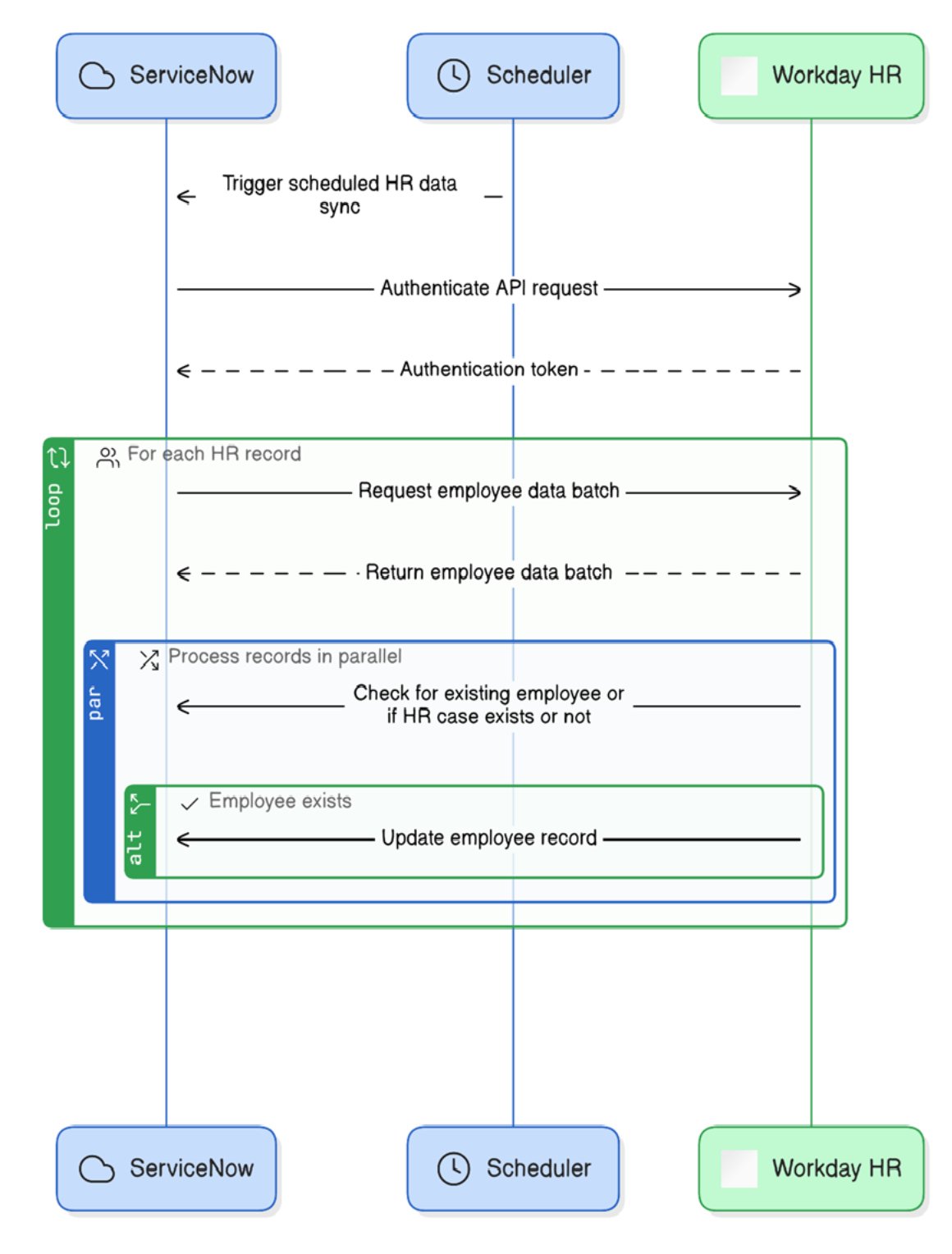
ServiceNow - Workday Integration
- Uses the Workday HR Spoke for seamless integration between Workday HCM and ServiceNow.
- Authentication is handled via OAuth 2.0, ensuring secure and modern authorization for API communication.
- The spoke leverages SOAP‑based Workday APIs, which ServiceNow uses to pull delta data based on specific Workday business processes (such as hire, termination, or job change).
Challenges
Implementing Service Now is not as easy as it sounds. We faced couple of challenged that we think are interesting to share.
Complex Customization
Implementing ServiceNow requires strong collaboration between IT, business teams, and end-user experience groups. Often, ITSM initiatives are perceived as “extra work” or non-productive by business applications. The biggest challenge was securing buy-in from stakeholders who saw this as a disruption rather than an enabler. Demonstrating the value of ServiceNow—such as faster resolution times and improved visibility—was key to overcoming this resistance.
Cost Management and example outcome
One of the less obvious but critical challenges we faced was managing the overall cost of implementing and maintaining ServiceNow. While the platform offers immense value, its licensing model can become expensive as more modules and users are added. Additionally, implementation costs—such as customization, integration, and professional services—can escalate quickly if not carefully controlled.
We realized early on that without strict governance, costs could spiral beyond initial estimates. To address this, we implemented a cost-control strategy that included:
- Clear Scope Definition: Avoiding unnecessary modules and focusing on high-impact features first.
- Governance Framework: Establishing approval processes for new customizations and integrations to prevent scope creeping.
- Regular Cost Reviews: Monitoring license utilization and optimizing user roles to avoid paying for unused capacity.
- Vendor Negotiation: Leveraging Michelin’s global scale to negotiate better terms with ServiceNow and implementation partners.
Decision Criteria
- Cost Visibility – Real-time dashboards for IT and operational spend by region and plant.
- Automation – Automated approvals, chargebacks, and invoice processing to reduce manual effort.
- Compliance – Role-based access, audit trails, and adherence to Michelin’s financial policies.
- Forecasting – AI-driven predictions for maintenance and IT budgets to optimize spend.
Example Outcome could be
- Track IT costs per plant in a single dashboard.
- Predict next quarter’s maintenance spend using AI.
- Enforce financial governance through approval workflows.
Processes – Complex, Missing, or Non-Uniform
ServiceNow relies heavily on well-defined processes for incident, change, and request management. During implementation, we discovered that many processes were either too complex, inconsistent across regions, or poorly documented. We had to work closely with stakeholders to simplify and standardize these processes. In most cases, this exercise resulted in better and more efficient workflows than what existed before.
Integration with Legacy Systems
One of the toughest technical challenges was integrating ServiceNow with older applications and infrastructure. These systems often lack modern APIs or have region-specific customizations, making integration time-consuming and error prone. We had to design robust connectors and data validation mechanisms to ensure consistency and reliability.
What we are exploring now
We are doing a proof of concept with Service-now to transform daily IT operations by bringing automation, intelligence, and real‑time context into the workflow. ServiceNow plays a central role in this ecosystem by serving as the backend platform that provides operational data such as incidents, CMDB relationships, and service offerings. Using its native APIs and adaptors, ServiceNow functions as an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server, supplying high‑quality contextual information that AI systems can use for analysis and decision‑making. GitHub Copilot could act as the MCP client, consuming this context to interpret issues, suggest remediation steps, and automate routine queries.
Early proof‑of‑concepts—like Service Operations Workspace, Virtual Agents, and Recommended Actions—already demonstrate the potential of this integration. Looking ahead, ServiceNow’s NOW Assist Skills will evolve to operate as full MCP servers, enabling deeper context delivery and more autonomous, intelligent AIOps capabilities. Together, these technologies drive faster, smarter, and more proactive IT operations.
Stay tuned ;)

